Endovascular Therapies
Endovascular procedures are minimally invasive treatments for blood vessel conditions, performed using catheters and imaging techniques. They offer advantages like smaller incisions, less pain, quicker recovery, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery. These procedures are used to treat a variety of vascular diseases, including peripheral artery disease, aneurysms, and other conditions affecting blood vessels.
- Access: A small incision or needle puncture is made in the skin, typically in the groin or arm, to access a blood vessel.
- Catheter Insertion: A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the blood vessel and guided through it to the area needing treatment.
- Imaging Guidance: Advanced imaging techniques like X-rays or fluoroscopy are used to guide the catheter and ensure it reaches the correct location
- Imaging Guidance: Advanced imaging techniques like X-rays or fluoroscopy are used to guide the catheter and ensure it reaches the correct location.
- Intervention: Various interventions can be performed using the catheter, such as angioplasty (opening a narrowed artery), stenting (placing a small tube to keep an artery open), or embolization (blocking a blood vessel).
- Intervention: Various interventions can be performed using the catheter, such as angioplasty (opening a narrowed artery), stenting (placing a small tube to keep an artery open), or embolization (blocking a blood vessel).
How do Endovascular Procedures Work:
Aneurysm Repairs
- EVAR (Endovascular Aneurysm Repair)
- Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR)
- TEVAR (Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair)
- Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to manage abdominal aortic aneurysms. The aorta is the largest artery that carries blood from your heart to other parts of your body. For abdominal aortic aneurysms, EVAR uses small punctures and sophisticated instruments to repair bulges in blood vessels (aneurysms) located there.
- The goal of endovascular aneurysm repair is to prevent the abdominal aortic aneurysm from bursting, which is a life-threatening event.
The force of blood flow against a weak spot in the wall of the blood vessel (here the aorta) causes the aortic walls to balloon outward, creating an aneurysm. This can lead to a burst, disrupting blood flow to your organs. Life-threatening complications can occur in minutes.
EVAR lowers the chances of a rupture by re-lining the aneurysm with a new tube, which takes the pressure off the aneurysm. The tube is called a stent graft, and it’s made of fabric with a metal mesh frame.
What is endovascular aneurysm repair?
Why might I need EVAR?
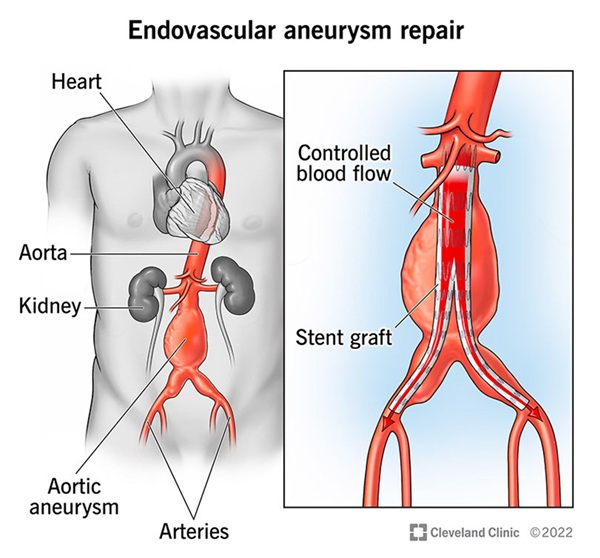
- You may benefit from EVAR if you have an aortic aneurysm. Aortic aneurysms affect the body’s largest artery, the aorta.
- Not all aneurysms need treatment. Your Doctor may consider EVAR if you:
1)Have a large aneurysm or smaller aneurysm that’s growing quickly.
2)Do not qualify for open surgery with a large incision.
3)Have healthy blood vessel tissue near the aneurysm. - Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR) is a specialized EVAR technique that repairs complex aneurysms. Your abdominal aorta is like a tree trunk that has many branches coming out of it. These branches are the arteries that carry blood to organs in your belly. If an aneurysm occurs near one of those branching points, it’s harder to treat. That’s where FEVAR comes into play.
- FEVAR uses a fenestrated stent graft, meaning a graft with small openings. Those openings give rise to additional stent grafts that go into branching arteries. This special device fits the tree-like structure of your aorta and its branches. EVAR, by comparison, uses a graft that doesn’t have little openings for branches. It’s a standard tube shape.
- Your Interventional Cardiologist will decide which procedure you need depending on where your aneurysm is located.
- EVAR treats aneurysms in your abdomen (belly). Thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair (TEVAR) treats aneurysms in your thorax (chest). TEVAR is especially suited to treat aneurysms in your descending aorta – the part that moves down through your chest toward your belly. Aneurysms very close to your heart, in your aortic root or ascending aorta, usually require open surgery.
- As a minimally invasive procedure, EVAR is gentler on your body. Benefits include:
1)Fewer days in the hospital.
2)Less blood loss.
3)Less discomfort during recovery.
4)Quicker return to daily activities.
5)Reduced risk of a having a heart attack or dying around the time of your procedure than you’d have in open surgery.
6)Shorter procedure time than open surgery.